Power Distribution: The Backbone of Modern Energy Systems
Electric power distribution is a critical component of the power delivery infrastructure, responsible for ensuring that electricity reaches consumers safely and efficiently. It acts as the intermediary between high-voltage transmission networks and end-users, such as homes, businesses, and industries.
Table of Contents :
- What is Electric Power Distribution?
- Voltage Levels in Power Systems
- Power Transmision vs Power Distribution
- The Importance of Reliable Power Distribution
- Case Study: The 2003 North American Blackout
- Illustration Power Distribution in Hospitals
- Types of Distribution Systems
- Conclusion

Design and System of Power Distribution by PT Media Kontrol Utama
1. What is Electric Power Distribution?
Electric power distribution refers to the network of substations, transformers, and power lines that transport electricity from high-voltage transmission systems to residential, commercial, and industrial consumers. It typically operates at voltage levels below 35 kV, distinguishing it from high-voltage transmission systems that transport electricity over long distances.
At the heart of the distribution system lies the distribution substation, where transmission-level voltage (35 kV to 230 kV) is stepped down by transformers into medium voltage (600 V to 35 kV). From here, electricity travels through primary distribution lines before reaching distribution transformers, which further reduce the voltage to a level suitable for consumer use, typically 120/240 V.
2. Voltage Levels in Power Systems
Understanding the various voltage levels in power systems provides clarity on how electricity moves from generation to consumption:
- Generation: 1 kV – 30 kV
- Ultra High Voltage Transmission: 500 kV – 765 kV
- High Voltage Transmission: 230 kV – 345 kV
- Sub-transmission System: 69 kV – 169 kV
- Distribution System: 120 V – 35 kV
3. Power Transmission vs. Power Distribution
The key difference between transmission and distribution lies in voltage levels and the distance electricity travels:
Transmission: Functions like an “interstate highway,” transporting high-voltage electricity over long distances from power plants to substations.
Distribution: Acts like “city streets,” delivering lower-voltage electricity from substations to end-users.
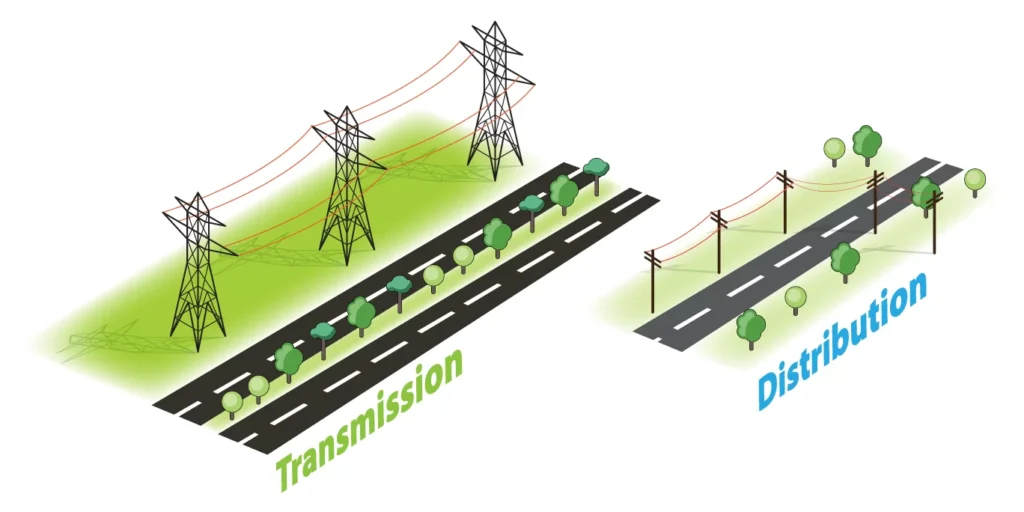
Source : Power Transmission vs Distribution – YSG Solar
4. The Importance of Reliable Power Distribution
A reliable power distribution system is essential for modern society. It ensures:
Uninterrupted Service: Power outages can disrupt daily life, hinder business operations, and compromise critical infrastructure such as hospitals and communication networks.
Safety and Stability: A stable distribution system minimizes voltage fluctuations and prevents electrical hazards that could damage equipment or endanger lives.
Economic Productivity: Industries and businesses rely on a consistent power supply to maintain production, efficiency, and competitiveness.
Support for Technological Growth: As smart grids, renewable energy sources, and electric vehicles become more widespread, a robust power distribution network is crucial for integrating these advancements smoothly.
Disaster Resilience: A well-planned and maintained power distribution system can withstand natural disasters and other emergencies, ensuring quick recovery and minimizing downtime.
5. Case Study: The 2003 North American Blackout
One of the most significant examples of why reliable power distribution is crucial is the 2003 North American Blackout. This massive power outage affected over 50 million people in the United States and Canada, causing billions of dollars in economic losses. The primary cause was a failure in the power distribution system due to a combination of software issues, human error, and inadequate grid maintenance. The blackout led to:
- Major disruptions in public transportation, water supplies, and emergency services.
- Shutdown of thousands of businesses, including financial markets and manufacturing plants.
- Increased risks for hospitals and critical care facilities relying on backup power.
6. Illustration: Power Distribution in Hospitals
Hospitals rely heavily on a stable and continuous power supply. A sudden power outage in a hospital can be life-threatening, affecting:
- Surgical operations: Modern surgeries depend on high-tech equipment such as anesthesia machines, heart-lung bypass machines, and robotic surgical tools. A power failure during an operation can cause critical delays, endangering patients’ lives.
- Medical devices: Many patients rely on ventilators, dialysis machines, and infusion pumps that require an uninterrupted power supply. Even brief power interruptions can compromise patient care and recovery.
- Data storage: Electronic medical records, diagnostic imaging systems, and automated laboratory equipment are essential for efficient hospital operations. Power failures can lead to data corruption, loss of critical patient information, and delays in treatment decisions.
To mitigate these risks, hospitals implement redundant power distribution systems with emergency backup generators, uninterruptible power supplies (UPS), and smart grid technology to ensure an uninterrupted power supply.
7. Types of Distribution Systems
Power distribution systems vary based on industry needs and operational requirements. These include centralized, decentralized, and combined distribution systems.
Centralized Distribution Systems
A centralized distribution system is a structured approach to power distribution where all electrical loads are connected to a central power source. This system is commonly used in large industrial facilities, manufacturing plants, and continuous process industries, where uninterrupted power supply and centralized monitoring are critical.
How It Works:
- Power is distributed from a central substation or power hub to different sections of a facility.
- The distribution is managed through a structured network of cables, switchgear, and transformers.
- Power control and monitoring systems ensure stability and efficiency.
Used in industries requiring continuous processes, such as:
- Cement plants
- Oil and gas
- Petrochemicals
- Steel and paper industries
Advantages with Centralized Distribution Systems:
- Ensures continuity of service
- Provides combined power, control, and monitoring circuits
- Allows for remote supervision
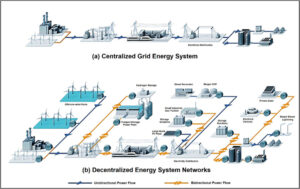
Distributed energy systems A review of classification, technologies, applications, and policies – ScienceDirect
Decentralized Distribution Systems
A decentralized distribution system distributes electricity using multiple smaller power distribution units located close to the point of use, rather than relying on a single central substation. This system is widely used in industries requiring flexibility, modular expansion, and independent operation of different sections of a facility.
How It Works:
In a decentralized system, power is distributed across several localized transformers and distribution centers, allowing for independent operation of different sections. This setup minimizes long power transmission lines within a facility and ensures localized power control.
Advantages of Decentralized Distribution Systems
1. Flexibility in Design and Expansion:
- Unlike centralized systems that require detailed pre-planning, decentralized distribution allows industries to modify and expand their power system without disrupting the entire operation.
- Ideal for industries with frequently changing layouts or production lines.
2. Improved Reliability and Reduced Downtime:
Since power is distributed across multiple smaller transformers, a failure in one section does not necessarily affect the entire system.
Industries can continue operations in unaffected areas while maintenance is performed on faulty sections.
3. Faster Installation and Lower Initial Costs:
- Since power distribution is done locally, the need for extensive cabling and infrastructure is reduced.
- This results in lower installation costs and faster deployment.
4. Optimized Energy Efficiency:
- Decentralized systems reduce transmission losses because electricity does not have to travel long distances within a facility.
- This leads to better energy management and lower operational costs.
Industries That Benefit from Decentralized Distribution
Decentralized power distribution is ideal for industries with varied power needs across different sections of their facilities, including:
- Mechanical Manufacturing: Factories with different production zones requiring independent power sources.
- Textiles and Lumber Industries: Facilities where sections operate independently with varying power demands.
- Injection Molding and Electronics: Industries that need to rapidly modify production lines.
- Pharmaceuticals and Livestock Farming: Facilities requiring stable power for sensitive production processes.
For example, an electronics manufacturing plant may have different sections for assembly, testing, and packaging, each with unique power requirements. A decentralized system allows these sections to operate independently without affecting the entire facility if a fault occurs.
Combined Distribution Systems
A combined distribution system integrates the advantages of both centralized and decentralized distribution systems, offering flexibility, reliability, and efficiency. This hybrid approach is ideal for industries and facilities that require both continuous power supply and modular expansion capabilities.
How It Works
In a combined distribution system, certain critical loads or primary areas operate under a centralized model, while other sections with varying power demands use a decentralized setup. This allows for efficient power management, improved fault tolerance, and easier system expansion.
For example, in a large industrial complex, high-demand machinery and essential infrastructure (such as control rooms) may rely on a centralized power source, while production lines or modular workstations use decentralized distribution for adaptability.
Advantages of Combined Distribution Systems
1. Balanced Power Distribution:
Ensures a stable power supply for critical operations while allowing flexibility in areas that require frequent modifications.
2. Higher Reliability and Redundancy:
Centralized systems provide uninterrupted power for mission-critical operations, while decentralized elements prevent localized failures from disrupting the entire system.
3. Scalability for Future Expansion:
Facilities can expand their operations without overhauling the entire power distribution network.
4. Optimized Cost and Efficiency:
Reduces infrastructure costs by centralizing major loads while minimizing transmission losses through decentralized components.
Industries That Benefit from Combined Distribution Systems
This approach is widely used in facilities that require both stability and adaptability, such as:
1. Commercial and Service Buildings:
Offices, retail stores, hospitals, and exhibition centers where different sections have varying power needs.
2. Infrastructure Projects:
Airports, telecommunications hubs, data centers, and tunnels that require both continuous power supply and adaptable distribution for different systems.
3. Industrial Facilities:
Pharmaceutical and food processing industries, where critical operations need uninterrupted power while production areas must accommodate flexible workflows.
For instance, a modern hospital may use a centralized system to power critical care units, operating rooms, and life-support systems, while a decentralized system supports outpatient departments and administrative offices. This ensures a stable and efficient power supply tailored to each section’s needs.
Conclusion
Electric power distribution plays a vital role in delivering electricity safely and efficiently to end-users. By understanding the different distribution systems and their applications, industries can optimize their power usage and improve operational reliability.
Whether centralized, decentralized, or a combination of both, selecting the right distribution system is key to maintaining an efficient and resilient power infrastructure. The importance of a reliable power distribution network cannot be overstated, as demonstrated by real-world incidents such as the 2003 blackout and the critical needs of hospitals and industries worldwide.
Recommendation: Expert Electrical Solutions by PT Media Kontrol Utama
Ensuring a reliable and efficient power distribution system requires expertise in electrical design, installation, and maintenance. Whether you need a centralized, decentralized, or combined distribution system, working with the right professionals can help optimize your power infrastructure for maximum efficiency and reliability.
At PT Media Kontrol Utama, our team of electrical experts specializes in:
✅ Power system design & consultation
✅ Installation & maintenance of distribution networks
✅ Energy efficiency solutions
✅ Smart grid integration & automation
With extensive experience in industrial, commercial, and infrastructure projects, we provide tailored solutions to meet your specific power distribution needs.
Talk With Us :
Reference :
- IOWA State University
EE 653 Power distribution system modeling, optimization and simulation: Introduction to Power Distribution Systems by Dr. Zhaoyu Wang. Accessed 08 March 2025. - Wikipedia
Electric Distribution. Accessed 09 March 2025. - YSG Solar
What’s the Difference Between Transmission and Distribution Power Lines? | YSG Solar. Accessed 11 March 2025.
- CBC Radio Canada
The great North America blackout of 2003. Accessed 11 March 2025 - ScienceDirect
Distributed energy systems: A review of classification, technologies, applications, and policies. Accessed 12 March 2025



